
The Debezium team is excited to announce the immediate availability of Debezium 3.3.0.Final. This release includes a myriad of features including the new Debezium Quarkus Extension, providing seamless integration for Debezium with PostgreSQL in Quarkus, support for Apache Kafka 4.1, exactly-once support for all core connectors, OpenLineage support for MongoDB and JDBC sink connectors, and so much more!
In this post, we’re going to take a deep dive into all the changes in Debezium 3.3, discussing new features, and explaining all the possible changes that could have any impact to your upgrade process. As always, we recommend you read the release notes to learn about all the bugs that were fixed, update procedures, and more.
Breaking changes
With any new release of software, there is often several breaking changes. This release is no exception, so let’s discuss the major changes you should be aware of before upgrading to Debezium 3.3.0.Final.
Debezium core
Deprecated snapshot modes removed
In Debezium 2.6, we aligned the names of snapshot modes with their intended functionality, which included:
-
Deprecated
schema_only_recoveryand replaced withrecovery. -
Deprecated
schema_onlyand replaced withno_data.
Starting with Debezium 3.3, both schema_only_recovery and schema_only have been removed (DBZ-8171). Connector configurations that still rely on the deprecated modes will cause invalid configuration errors after upgrading, so it’s important to adjust your connector configurations accordingly.
Debezium Engine class loader changes
Debezium Engine did not set thread context classloader which could complicate integration with projects like SpringBoot. The thread context classloader is now set and Debezium Engine uses provided classloader to load all classes, not only the connector (DBZ-9375).
Debezium JDBC sink
JDBC sink data type precision changes
The upgrade to Hibernate 7.1.0.Final brings more precise data type handling, particularly for temporal and floating-point data (DBZ-9481):
- Temporal Types
-
The
timeandtimestampcolumns now default to higher precision. For example, Oracle time and timestamp columns will be created using 9-digit precision instead of the previous default of 6-digits. - Floating-point Types
-
Debezium explicitly prefers
float,real, anddouble precisionfor representing floating-point values. If you need Oracle’s binary float and double data types instead, sethibernate.dialect.oracle.use_binary_floatstotruein your connector configuration.
| Only new temporal type columns will be added using the new 9-digit precision while existing columns are unaffected. If you’d prefer your existing columns to be defined with the higher precision for consistency, this must be done manually. |
Debezium for Db2
Offset position validation is unreliable
Due to reliability issues with offset position validation in Db2, we’ve temporarily disabled validation to prevent false failures (DBZ-9470). As a result, the when_needed snapshot mode is currently unavailable for Db2 connectors.
Impact: If you’re using when_needed snapshot mode with Db2, you will need to use an alternative mode until this limitation is resolved in a future release.
Debezium for Cassandra
Cassandra JMX metrics have changed
In previous iterations of the Debezium for Cassandra connector, each JMX metric was exposed as different MBeans in the <logical-name> domain, with an example shown below:
#domain = <logical-name>:
<logical-name>:name=commitlog-filename
<logical-name>:name=commitlog-positionThis approach significantly differs from other connectors where the metrics implementation has a single domain with multiple MBeans, i.e.:
#domain = debezium.cassandra:
debezium.cassandra:context=snapshot,server=<logical-name>,type=connector-metrics
debezium.cassandra:context=streaming,server=<logical-name>,type=connector-metricsNow any metric that pertains to snapshot will be in the snapshot MBean and those for streaming are in the streaming MBean (DBZ-9281). Using the commitlog-filename as an example, it is now in the streaming MBean as CommitLogFilename.
| Please see the Cassandra documentation for all details about the new JMX metrics names. |
New features and improvements
The following describes all noteworthy new features and improvements in Debezium 3.3.0.Final. For a complete list, be sure to read the release notes for more details.
Debezium Core
Kafka 4.1.0 foundation for better performance
Debezium 3.3.0.CR1 is built against Kafka Connect 4.1.0 and has been thoroughly tested with Kafka brokers version 4.1.0 (DBZ-9460). This ensures Debezium can run on the latest, most stable Kafka infrastructure.
| Before upgrading, review the Kafka documentation to ensure compatibility with your existing Kafka broker versions. |
Exactly-Once Semantics support
There has been numerous requests from the community about Debezium with exactly-once semantics support. Exactly-once semantics in layman’s terms means that an event should only ever be delivered and written to a Kafka topic once, therefore avoiding the possibility of duplicates.
We are pleased to share that Debezium 3.3 introduces support for exactly-once semantics for all core connectors, including MariaDB, MongoDB, MySQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server (DBZ-9177).
Disabling context headers
In Debezium 3.2, we introduced several new headers to provide context for OpenLineage that are automatically added to every emitted event. Some users reported concerns with these being added with no way to disable them, as some environments had the need to keep event payloads as lean as possible.
Based on community feedback, we have introduced a new configuration option, extended.headers.enabled, that can be set to false, disabling the addition of these context event headers (DBZ-9248).
Heartbeats are no longer emitted constantly
In Debezium 3.3.0.Alpha1, users reported problems when using heartbeat.action.query that Debezium was emitting heartbeat events constantly regardless of the configured interval. This regression is fixed and heartbeat.action.query should now honor the configured heartbeat.interval.ms once again (DBZ-9340).
Connector startup fails with cryptic error
We’ve resolved an issue where connectors would fail to start with a misleading error message, restoring smooth startup while preserving improved offset validation.
Users began encountering this confusing exception during connector startup in one corner case:
org.apache.kafka.connect.errors.DataException: Invalid value: null used for required field: "schema", schema type: STRINGThis cryptic error message provided no useful information about what was actually wrong, making troubleshooting nearly impossible.
The issue was an unintended consequence of a recent improvement we made to offset validation. We enhanced the logic to provide better error messages when offset positions are no longer available in the source database—a valuable feature that helps diagnose common operational issues.
However, the new validation logic made assumptions about certain offset attributes being available during connector startup. In reality, these attributes aren’t populated until later in the connector’s lifecycle, causing the validation to fail prematurely with an unhelpful error message.
We’ve updated the exception handling logic to:
-
Avoid assumptions about offset attribute availability during startup
-
Preserve the enhanced validation for cases where offsets are genuinely invalid
-
Provide meaningful error messages when offset positions are actually problematic
-
Allow normal startup to proceed without false positives
This fix ensures you get the benefits of enhanced error reporting without the startup disruption (DBZ-9416).
Possible data loss after failed ad-hoc blocking snapshots
We’ve resolved a critical issue that could cause data loss when ad-hoc blocking snapshots encountered problems, ensuring your streaming data remains intact even when snapshots fail.
When running ad-hoc blocking snapshots, encountering invalid data in a table would cause the snapshot to fail. Unfortunately, this failure had a serious side effect: streaming events that occurred during the snapshot period were permanently lost.
This meant that if your snapshot ran for several hours before hitting bad data, all the real-time changes that happened during those hours would be skipped entirely when the connector resumed normal streaming operations.
Blocking snapshots now handle failures gracefully by:
-
Preserving the streaming position from immediately before the snapshot began
-
Automatically resuming from the correct position when the snapshot fails
-
Ensuring zero data loss regardless of when or why the snapshot encounters issues
This improvement makes blocking snapshots much more reliable for production environments (DBZ-9337).
Debezium for MongoDB
Start from a specific position
Debezium users can now start the MongoDB source connector at a specific position in the MongoDB oplog by specifying a new connector configuration property, capture.start.op.time, in the connector configuration. This new configuration property should be a long data type value that represents the Bson timestamp (DBZ-9240).
| Leaving this configuration property in the connector configuration will result in the connector attempting to resume from the specified position when restarted. It’s recommended when using this feature that once the connector begins to stream changes the property is removed so that any future restarts will honor the resume position present in the connector offsets instead. |
MongoEventRouter supports custom tracing values
The MongoEventRouter now supports the ability to pass custom tracing configuration values into the router so they’re made available in the event payload (DBZ-9328). The following configuration options can be provided:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| THe name of the field containing |
| The operation name representing the Debezium procesing span, defaulting to |
| Set to |
Debezium for MariaDB
MariaDB 11.7+ vector data type support
MariaDB 11.7 introduced the VECTOR(n) data type, allowing the storage of values in the relational database as if it were a vector database. Vector values that are generated by an AI model can be stored and searched in MariaDB using this new data type.
Debezium 3.3 introduces MariaDB vector data type support in the MariaDB source connector and the JDBC sink connector when writing to a MariaDB target database (DBZ-8582).
Schema history improvements
The MariaDB schema history topic is used by the connector to store a variety of DDL operations captured from the binary logs, allowing the connector to build a relational model from the chronological history of schema changes for tables.
In Debezium 3.3, the schema history topic’s filters were updated to avoid storing specific statements in the topic that are not relevant to Debezium’s function, such as procedure, function, view, trigger, and grant/revoke statements (DBZ-9186).
| For new connectors, such statements will not be stored. For existing connectors, only newly captured DDL statements that match the improved filters will be omitted, existing topic events are not removed. |
Debezium for MySQL
Schema history improvements
The MySQL schema history topic is used by the connector to store a variety of DDL operations captured from the binary logs, allowing the connector to build a relational model from the chronological history of schema changes for tables.
In Debezium 3.3, the schema history topic’s filters were updated to avoid storing specific statements in the topic that are not relevant to Debezium’s function, such as procedure, function, view, trigger, and grant/revoke statements (DBZ-9186).
| For new connectors, such statements will not be stored. For existing connectors, only newly captured DDL statements that match the improved filters will be omitted, existing topic events are not removed. |
Debezium for PostgreSQL
Text-search vector support
In PostgreSQL 13+, full text search data types were added. The tsvector data type represents a document in a form optimized for text searches, providing a sorted list of distinct lexemes.
With Debezium 3.3, you can now capture changes made to columns using the tsvector data type (DBZ-8470). These column types are emitted using the logical type called io.debezium.data.Tsvector and is represented as a string data type in the event.
TSVECTOR data type support in JDBC sink
In Debezium 3.3.0.Alpha1 we introduced support for the text-search based vector data type called TSVECTOR as part of the PostgreSQL source connector (DBZ-8470). In this release, we’ve extended that support to the JDBC sink connector so that TSVECTOR values can be written to PostgreSQL targets (DBZ-8471). If the target is a non-PostgreSQL database, the value will be written into a character-based column instead.
Publication DDL timeout
While we generally do not document internal configuration properties, we did add a new internal PostgreSQL connector configuration property internal.create.slot.command.timeout in the past to apply a set default timeout of 90 seconds when creating the connector’s replication slot. This was to address concerns with blocking transactions that would prevent the connector from advancing as a replication slot cannot be created while transactions are active.
We’ve extended the coverage for the timeout in Debezium 3.3 to apply to the DDL operations for creating and altering the PostgreSQL connector’s publication (https://issues.redhat.com/browse/DBZ-9310). If you notice timeouts creating/updating the publication or the slot, you may want to increase this configuration property (defaults to 90) or set it to 0 to disable the timeout feature.
Improved TOAST-column performance
The Debezium for PostgreSQL pgoutput decoder uses a specific pattern to determine whether a toasted column’s value matches a predefined list of marker objects that indicate the value is absent in the change event. However, this pattern was inefficient when the event payload contained large text or binary data, due to the cost of computing hash values before comparison.
To improve performance, the implementation now uses a direct equality check, avoiding expensive hash computations for large TOAST column payloads (DBZ-9345). This change reduces processing overhead when handling events with sizable text or binary data.
Only alter publication as needed
When a Debezium PostgreSQL connector is configured with publication.autocreate.mode set to filtered, the connector issues an ALTER PUBLICATION statement on each connector restart to guarantee that the publication remains aligned with the connector configuration.
In some cases where the underlying tables may be undergoing a vacuum or are involved in a long-running DDL operation, this will force the connector wait until those tasks complete before the alter can complete. In an effort to streamline this and to only block when absolutely necessary, the connector will now check the configured table list against the publication when using filtered mode. Only if there are differences in the table list will the alter command be executed, otherwise it is skipped to avoid potential blocking calls (DBZ-9395).
Debezium for Oracle
Legacy decimal handling mode behavior
In Debezium 2.7, we introduced a bug fix that aligned the behavior of decimal.handling.mode when using the double or string modes in the Oracle connector to match other relational connectors. This bug fix introduced a change in the event’s schema and created numerous problems for those upgrading who were not expecting such changes.
We looked at a variety of options, whether to introduce legacy support via a CustomConverter or a Transformation, however, we concluded that the legacy support needed to be baked into the connector to provide a sufficient solution.
In Debezium 3.3, a new configuration property legacy.decimal.handling.strategy was added allowing users to restore the use of the broken behavior, where numeric values with zero-scale would not be automatically converted to double or string and instead would be emitted as integer whole values as long as their length was 18 or less (DBZ-9166).
| If you are upgrading from a version prior to Debezium 2.7, it’s recommended you enable this feature at least initially to minimize the upgrade complexities to Debezium 3.3 or later. If you have already upgraded to Debezium 2.7 through 3.2, it’s not recommended to enable this legacy behavior as it will introduce the same schema change complexities but the inverse. |
LogMiner experimental CTE query support
We have introduced a new internal and experimental feature for Oracle LogMiner that leverages a concept called a CTE query, or a Common Table Expression query. A CTE query is a SQL construct that allows for the definition of a temporary, named result set within the execution of another SQL operation, which can be useful for a variety of reasons.
For the Debezium Oracle connector, the new internal.log.mining.use.cte.query feature toggles a special pre-pass that examines all transactions and performs a pre-filter pass (DBZ-9272). This filter pass is designed to only send START, COMMIT, and ROLLBACK events for transactions that actually contain at least one DML operation for a captured table. In other words, if someone performs 100 transactions and only one of those transactions modifies your captured table, then not only do we not receive the DML events for the other 99 transactions, but the transaction markers are also omitted, too.
| This feature is not without caveats, more notably the fact it requires two passes over the transaction logs. For systems where there is a disproportionately higher volume of changes in non-captured versus captured tables, the extra read pass may be worth it to minimize the network and connector processing overhead of extraneous transaction marker events. |
Last Batch Processing Throughput Metric Improved
We’ve enhanced the accuracy of the LastBatchProcessingThroughput JMX metric in the Oracle LogMiner adapter, giving you better visibility into your connector’s performance.
Previously, this metric calculated throughput based on the number of captured table events that were actually processed during each batch. While this seemed logical, it led to misleading results in several common scenarios:
-
Database-level filtering would reduce the count of processed events, even though the connector was still doing the work to read and evaluate those filtered records
-
Transaction markers in the event stream could skew the numbers, sometimes dramatically understating the actual processing load
-
Various configuration settings would impact the metric in ways that didn’t reflect the connector’s true performance
The metric now measures throughput based on the physical number of JDBC rows read from the LogMiner dataset, regardless of whether those rows end up being:
-
Filtered out by your configuration in the JVM
-
Transaction control records
-
Events that don’t match your table or schema filters
This gives you a much more accurate picture of the raw processing power your Debezium connector is delivering during each batch processing window (DBZ-9399).
Smarter archive destination management
A new precedence-based archive destination strategy can be used for certain Oracle connector environments. Previously, users had to specify a single destination (i.e. LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST_2), which required manual configuration changes during failover scenarios when the new primary uses a different destination name.
Users can now configure multiple destinations in priority order using a comma-separated list (DBZ-9041). For example, LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST_1,LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST_2. The connector will intelligently select the first destination that is both local and valid, adapting to failover scenarios requiring no configuration change.
As an example, the Oracle primary instance uses LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST_1 and the standby uses LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST_2. Using the new priority order feature, the connector seamlessly switches from LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST_1 to LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST_2 when failover occurs.
| Please note that this is only useful when a standby environment becomes the new primary environment during a disaster-recovery failover scenario. This is not the same as when an Oracle Real Application Cluster (RAC) node becomes unavailable and the connector connects to the next available node on the cluster. In the latter, all nodes on the cluster share the same archive destination configuration and priority order doesn’t apply. |
Commit SCN provided in XStream events
All Debezium change events include a source information block by default. For Oracle, this block contains a commit_scn field, which represents the system change number (SCN) of the transaction’s commit event.
Previously, commit_scn was only populated when using Oracle LogMiner. With this release, we’ve extended support to Oracle XStream as well (DBZ-9497).
XStream no longer flushes invalid low watermarks
The Debezium Oracle XStream implementation must periodically flush an LCR position to the Oracle Outbound Server. This flush acts as a hint to Oracle that all changes prior to that position have been processed, similar to how PostgreSQL confirms LSNs to a replication slot.
Previously, due to the way offset flushing was handled, the Oracle Outbound Server could incorrectly report a failure when attempting to flush the low watermark, treating a valid position as invalid. This issue has now been fixed, and the Oracle Outbound Server will no longer falsely report invalid low-watermark positions (DBZ-8923).
Debezium for SQL Server
Heartbeat improvements
The heartbeat behavior in SQL Server will now emit heartbeat events during periods where there are no changes in the capture instances for CDC-based tables (DBZ-9364). This should help make sure that while the LSN continues to advance in the database due to changes to non-captured tables, the offsets remain synchronized.
Debezium JDBC sink
Self-heals against database errors
The JDBC sink connector now automatically retries SQL exceptions that occur during change processing, providing a crucial buffer for self-healing scenarios to improve the connector’s resilience (DBZ-7772).
This is particularly valuable in multi-task environments where concurrent writes to the same table might cause lock conflicts. Instead of failing completely or delegating the restart to the runtime,the connector now recovers from these transient issues itself, significantly improving the overall reliability of the connector.
Debezium for CockroachDB
New source connector for CockroachDB
A new CockroachDB connector that is experimental and in active development, lead by the community in conjunction with Cockroach Labs (DBZ-9289). This connector is built on top of CockroachDB’s change-feed subsystem, to capture row-level changes, and emit those as change events.
This new connector requires CockroachDB 25.2+ with the rangefeed option enabled and Java 21+. This connector is currently incubating and is under heavy development by the community.
If you’d like to get started with the connector, you can get the connector with these coordinates:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.debezium</groupId>
<artifactId>debezium-connector-cockroachdb</artifactId>
<version>3.3.0.Final</version>
</dependency>The documentation for this connector is still under development, but you can find information about its configuration options and how to use it in the repository’s README.
Debezium for Informix
Enhanced default value localization support
The Informix connector now handles locale-specific database configurations more intelligently (DBZ-9181). Instead of assuming a US locale, the connector properly parses locale-dependent values like DBMONEY, DBCENTURY, and DBDATE based on your actual database configuration.
This improvement ensures more accurate data capture across diverse international deployments and eliminates potential data parsing errors in non-US environments.
Debezium Server
Azure Event Hubs - Built-in hashing partition keys
Azure Event Hub’s partition keys are limited to a maximum of 128 characters. In the event that an event’s key results in a partition key that exceeds that limit, Debezium Server’s Azure Event Hubs sink adapter would throw a exception and the connector would terminate. This is less than desirable behavior and introduces constraints on source tables where it may not be possible to address at the source.
To address this concern, the Azure Event Hubs sink can be configured to use one of several hashing algorithms to adhere to the maximum partition key size while working with source data where the partition key would otherwise exceed the maximum allowed size (DBZ-9245).
To enable the Azure Event Hubs sink to use the built-in hashing for partition keys, the sink must be configured using the debezium.sink.eventhubs.hashmessagekey configuration property set to true (the default is false). When enabled, the debezium.sink.eventhubs.hashmessagekeyfunction can be set to java (the default), md5, sha1, or sha256 to determine the type of hashing algorithm that’s used.
NATS Jetstream - Asynchronous event dispatch
The Debezium Server NATS Jetstream sink adapter previously relied on synchronous publishing, which imposes performance limitations for high volume streaming scenarios. In order to support high volume streaming scenarios, the NATS sink supports two new configuration options (DBZ-9474):
| Property | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
| Specifies whether the sink adapter should use asynchronous publishing. |
|
| The number of milliseconds before an asynchronous publish call fails due to timeout. |
In this release, the new asynchronous publishing feature is enabled by default but can be disabled by setting async.enabled to false.
| All Debezium sink adapter configurations have a unique prefix. Be sure to prefix these new configurations with |
Debezium Platform
New Smart Editor
Managing similar Debezium connectors across different runtimes presents its own unique sets of maintenance challenges since each runtime uses different formats, i.e. Kafka Connect with JSON versus Debezium Server with key/value properties files. The Debezium Platform also uses its own JSON-based format that differs slightly from Kafka Connect, which adds another layer of complexity.
New Connection Management
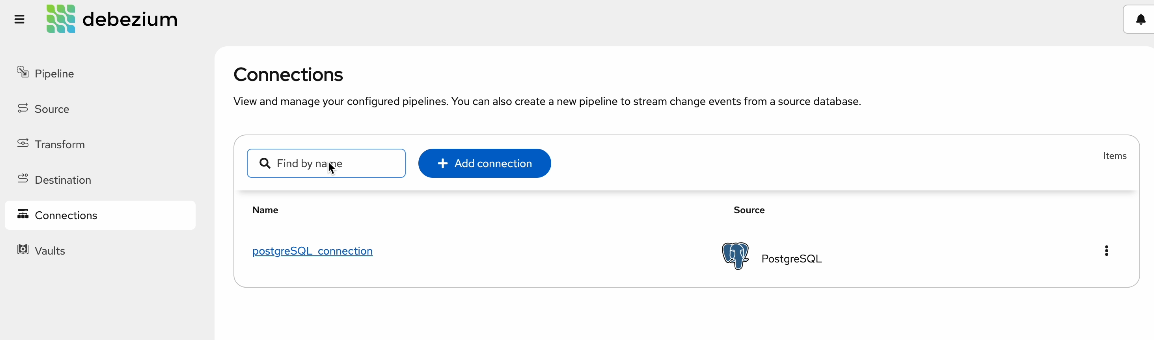
You can now manage connection credentials and details separately from sources and destination configurations (DBZ-9314). This simplifies the management of connections where you may have multiple pipelines that connect to the same source or destination system.
In this screenshot, you can see how you can manage and add new connections.
In this screenshot, you can see how you can view and edit the connection details.
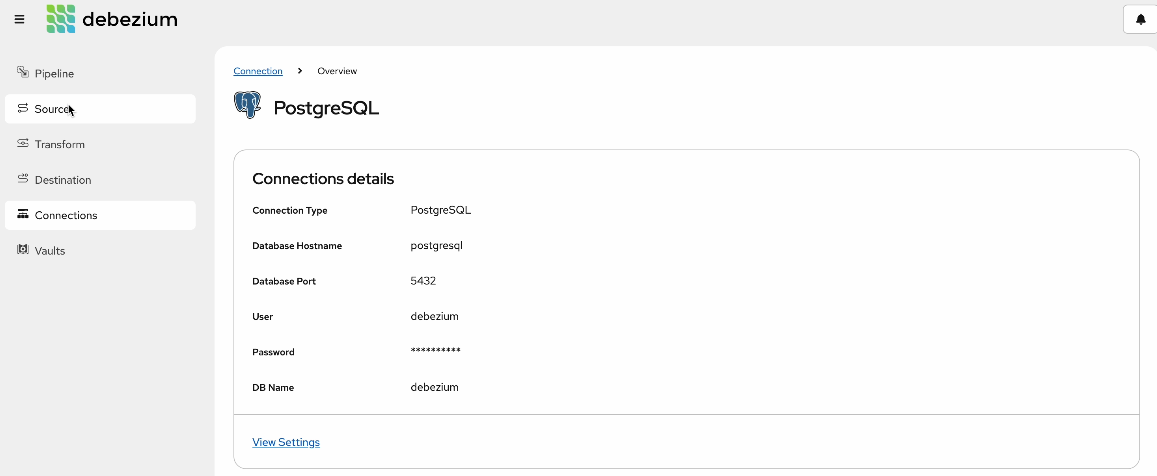
When creating new sources or destinations, you can pick whether you want to create a new connection or reuse an existing one for simplicity.
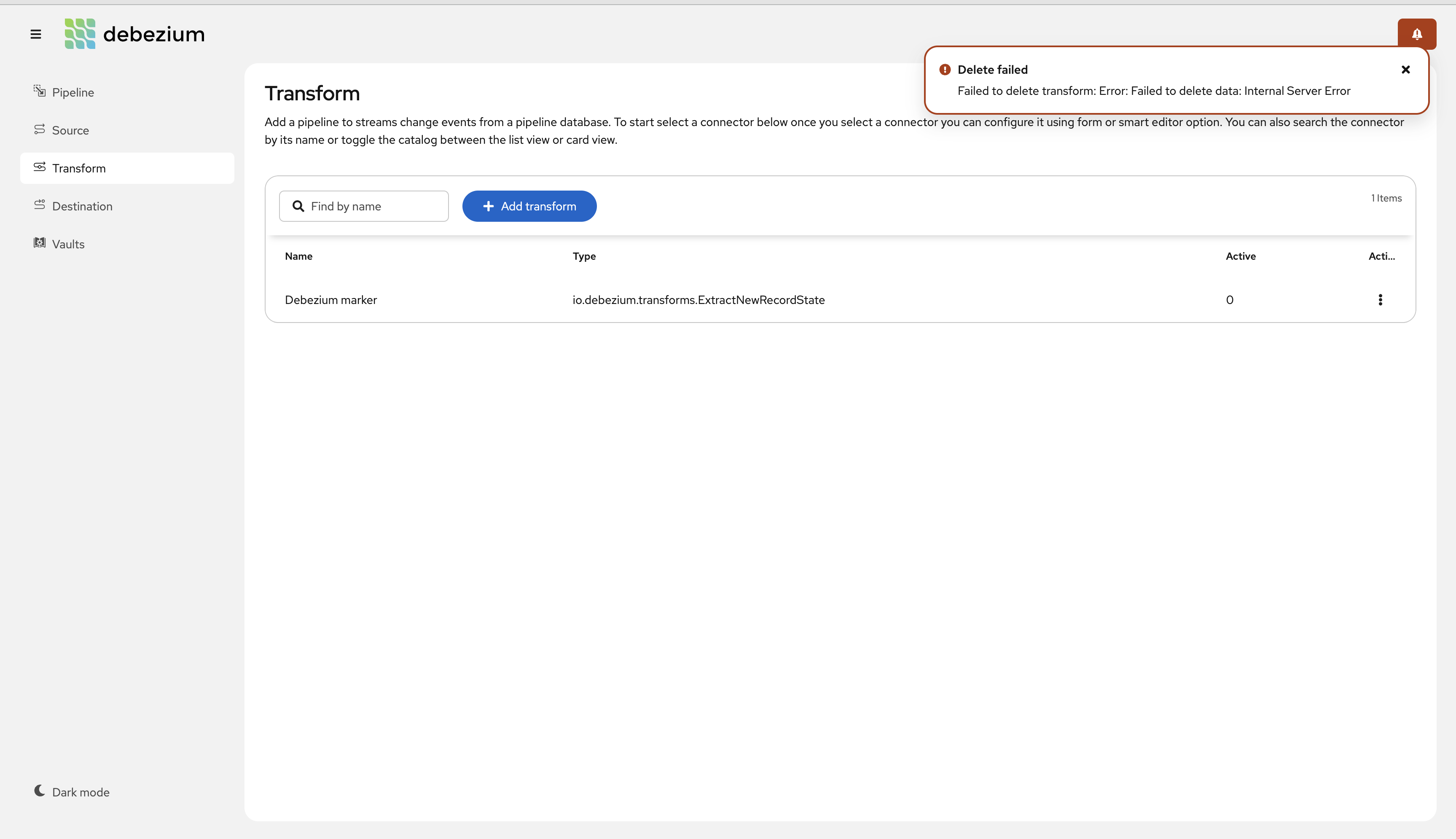
Error handling and messaging improvements
We’ve improved this process to provide significantly better descriptions to help users in the user interface (DBZ-8836), as shown here:
Configure logging in the User interface
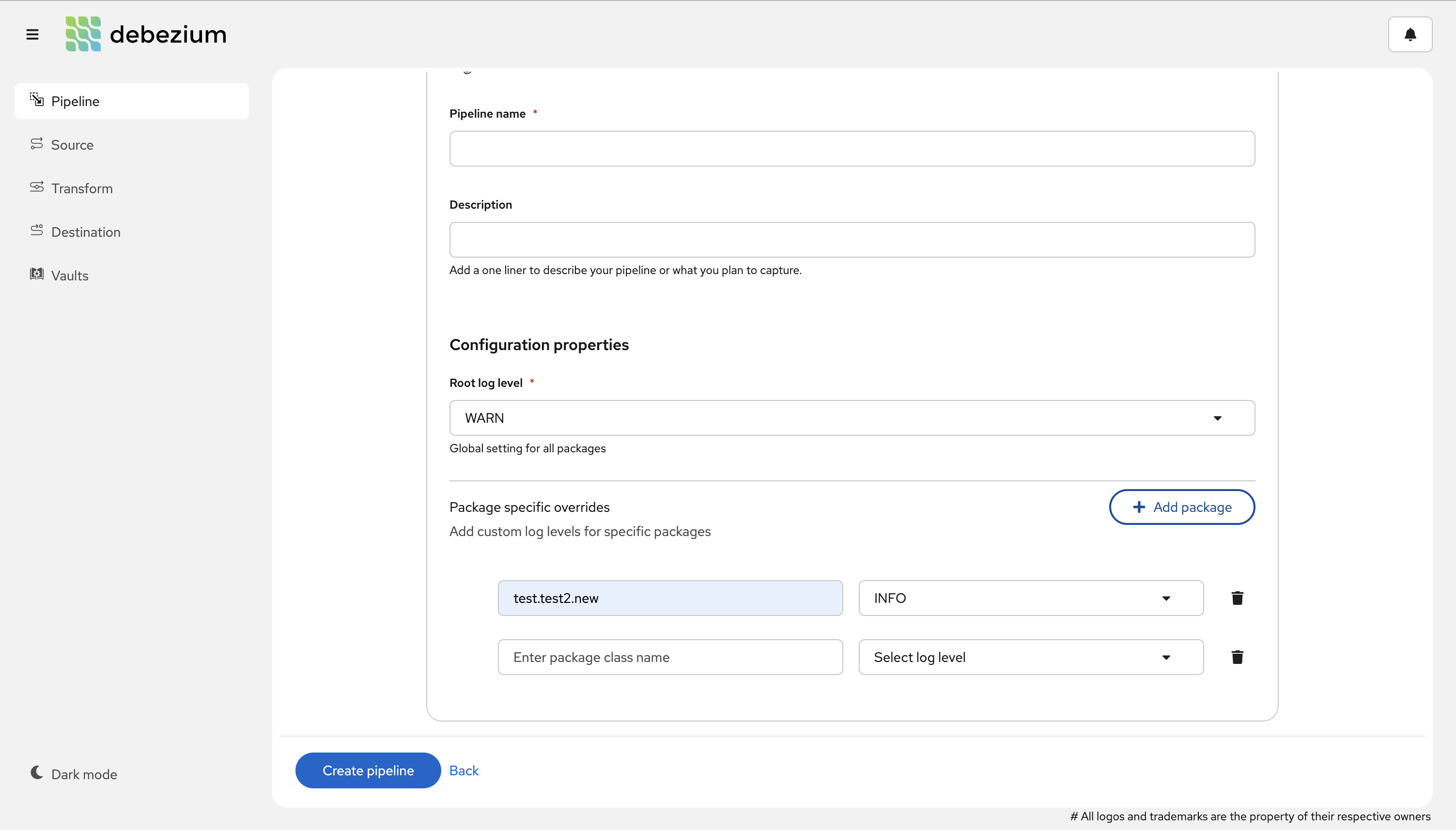
The Platform now provides users the ability to define fine-grained logging configuration as the user interface, which can be extremely useful when debugging or diagnosing a connector-related problem (DBZ-8890), seen here:
Source and destination improvements
There are some improvements around adding details when defining source and destination types (DBZ-9373). We’ve included a video below that outlines how these work
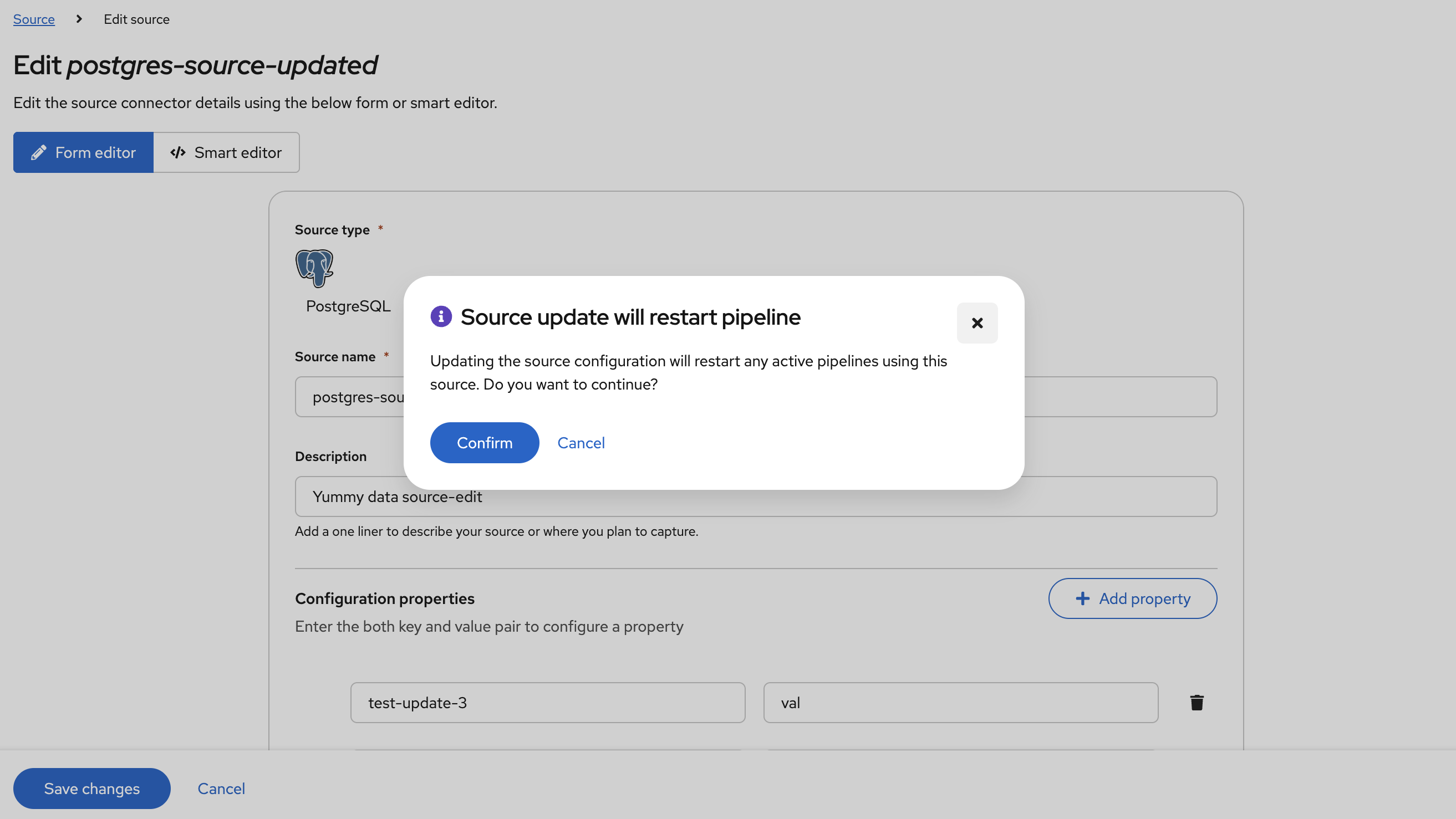
Notify users of pipeline restart on changes
When working with the Debezium Platform, a source, destination, or other resources may be shared across two or more pipelines. When making changes to these resources, any pipeline that makes use of that resource must be restarted for those changes to take effect.
In an effort to avoid unexpected outcomes due to pipeline restarts, Debezium Platform will notify users when making changes that could lead to a pipeline being restarted so that the updated configuration can be applied (DBZ-9104).
Debezium Quarkus Extension / Integration
One of the most recent additions to Debezium’s portfolio is the Debezium Quarkus extension, which enables developers to utilize Debezium’s CDC capabilities directly within a Quarkus-based application in either JVM or Native builds. We’ve added several new improvements, so let’s cover each of those separately.
Heartbeat listeners
Debezium can be configured with heartbeat.interval.ms to make Debezium emit a heartbeat event into the event stream periodically. Heartbeat events can be used for a variety of reasons, but their main use is to make sure that offsets remain aligned with the current read state on the source database, even during periods of low/no activity for captured tables.
A Quarkus application using the Debezium extension can also perform additional actions when a heartbeat is emitted by observing the CDI event DebeziumHeartbeat. This allows for application-specific code to be executed for each heartbeat (DBZ-8960).
In the following example, the listener merely writes to the console when a heartbeat is observed.
@ApplicationScoped
public class HeartbeatListener {
public void consoleHeartbeat(@Observes DebeziumHeartbeat event) {
System.out.println("Debezium emitted a heartbeat event!");
}
}Easily implement custom converters
A Debezium CustomConverter is a tool that can be used to change how Debezium emits the value for a given column type. This can be an extremely powerful for consumers that require data in a specific format.
Within your Quarkus application, you can use the traditional way to define a CustomConverter by specifying it as part of the connector configuration in your application.properties file; however, Debezium 3.3 adds a new annotation-based approach that simplifies configuration and makes iterative development much easier and faster (DBZ-8966).
As an example, the following showcases defining a converter that takes a given raw field and return’s its value converted as a String in the event using the Java toString() function.
@ApplicationScoped
class RawToStringConverter {
@CustomConverter
public ConverterDefinition<SchemaBuilder> bind(ConvertedField field) {
return new ConverterDefinition<>(SchemaBuilder.string(), Object::toString);
}
}In addition, custom converters can be selectively applied to fields. Developers may be inclined to implement this behavior in the custom converter annotated method, and while that’s valid, this can be done in a component-driven way using a FieldFilteringStrategy.
As an example, the following showcases the same custom converter, but uses the field filtering strategy:
@ApplicationScoped
class RawToStringConverter {
@CustomConverter(filter = CustomFieldFilteringStrategy.class)
public ConverterDefinition<SchemaBuilder> bind(ConvertedField field) {
return new ConverterDefinition<>(SchemaBuilder.string(), Object::toString);
}
}
@ApplicationScoped
class CustomFieldFilteringStrategy implements FieldFilteringStrategy {
@Override
public boolean filter(ConvertedField field) {
/* implement your selective logic here */
return false;
}
}CDC events as POJOs
The Debezium Quarkus extension emits change events as structured ChangeEvent<K, V> types. But in some situations, it may be useful to transform the change event into a Java record or a domain-specific POJO. For these cases, Debezium’s Quarkus extension provides a standardized way to deserialize a ChangeEvent into your Java record or POJO.
As an example, let’s assume we have a products table in our source where we have a capturing handler defined. In this handler, we’d like to process Product objects, as seen below.
@ApplicationScoped
class ProductHandler {
@Capturing(destination = "prefix.inventory.products")
public void captureProducts(Product product) {
/* do something with product */
}
}For this to work, a Deserializer<T> needs to be implemented to convert the ChangeEvent into our target POJO type Product. The extension provides an implementation to handle this using Jackson, ObjectMapperDeserializer.
public class ProductDeserializer extends ObjectMapperDeserializer<Product> {
public ProductDeserializer() {
super(Product.class);
}
}The last step involves defining the deserializing mapping in the Quarkus configuration to glue it all together.
quarkus.debezium.capturing.product.destination=prefix.inventory.products
quarkus.debezium.capturing.product.deserializer=<the-java-package>.ProductDeserializerThe extension will use this configuration to map an event destined for the prefix.inventory.products topic to use the product deserializer. This deserializer is mapped to the <the-java-package>.ProductDeserializer class, which uses Jackson to convert the ChangeEvent into a Product object. After the conversion, the @Capturing annotated method is called with the Product object instead of the emitted ChangeEvent.
Debezium Quarkus Outbox Extension
Supports latest Quarkus
The Debezium Quarkus Outbox extension relies on Hibernate for persistence like most Quarkus-based extensions, and in the latest Quarkus 3.23.x, the version of Hibernate was updated to 7.x. This new version of Hibernate introduced a variety of breaking changes that lead to the extension being incompatible.
With Debezium 3.3 (and backported to the upcoming Debezium 3.2.1), the Debezium Quarkus Outbox extension is compatible with the latest builds of Quarkus working with Hibernate 7+ (DBZ-9219).
| Due to the compatibility changes, when using Debezium 3.2.0.Final or earlier, the Quarkus application must be based on Quarkus 3.22.x or earlier. The use of Quarkus 3.24.x or later is only possible when using Debezium 3.2.1 / 3.3.x or later. |
OpenLineage Integration
Support for Debezium sink connectors
OpenLineage enables the capture of rich metadata from data pipelines. With this release, we’ve expanded the OpenLineage integration to cover both the JDBC and MongoDB sink connectors (DBZ-9469).
Other fixes
The following are just a subset of some noteworthy additional changes and fixes in Debezium 3.3:
-
Execute Debezium in oracle readonly replica DBZ-8319
-
A transaction mined across two queries can randomly cause unsupported operations DBZ-8747
-
Debezium Engine Quarkus Extension: introduce PostProcessor handler DBZ-8965
-
During a mining session treat ORA-00310 redo logs being inconsistent DBZ-8870
-
JdbcSchemaHistory Fails to Handle Data Sharding When Recovering Records DBZ-8979
-
Add JMX metrics/statistics for cached events DBZ-8991
-
'||' in ORACLE NVARCHAR data will cause exception DBZ-9132
-
When using non-recovery snapshot modes, offsets are not reset DBZ-9208
-
Incremental snapshot offset failing to load on task restart DBZ-9209
-
Validation for Log Position for SqlServer can fail DBZ-9212
-
Possible regression with throwing DebeziumException rather than warning DBZ-9217
-
Double event publishing via NATS Jetstream sink DBZ-9221
-
NullPointerException is thrown because DebeziumHeaderProducer is not registered DBZ-9225
-
MongoDB ExtractNewDocumentState SMT crash with nested struct in array in 3.2 DBZ-9231
-
Mongodb incremental snapshot is not honoring additional conditions DBZ-9232
-
Oracle snapshot boundary mode does not have a field display name DBZ-9236
-
Request fix for muti-task CREATE TABLE collisions for jdbc postgres target causing task to crash DBZ-9237
-
Exceptionally large mining windows can lead unintended metrics/performance issues DBZ-9241
-
Throw an exception on missing heartbeat table on Debezium-connector-postgres DBZ-9247
-
Allow Oracle heartbeat action query error handler to be resilient to ORA-02396 DBZ-9280
-
OpenLineage output dataset uses the wrong datatype DBZ-9285
-
Debezium platform verify signal data collection fails DBZ-9290
-
Unchecked exception from OffsetStorageWriter.doFlush() in AsyncEmbeddedEngine leaves semaphore in OffsetStorageWriter unreleased and probably causes engine to fail DBZ-9292
-
Reselect post processor does not work with VariableScaleDecimal primary keys DBZ-9293
-
Debezium Server Azure Event Hubs sink duplicates all previous events DBZ-9304
-
Duplicate key exception when using postgres connector based on pgoutput plugin DBZ-9305
-
Archive log only mode does not pause mining when no more data available DBZ-9306
-
Source and Destination entities must be linked to the Connection entity DBZ-9333
-
Events may be mistakenly processed multiple times using multiple tasks DBZ-9338
-
Allow redo thread flush scn adjustment to be configurable DBZ-9344
-
Fetching transaction event count can result in NullPointerException DBZ-9349
-
Ensure JAVA_OPTS env var is correct on dbz server startup DBZ-9352
-
Issue in ReselectColumnsPostProcessor when field’s schema type is BYTES DBZ-9356
-
Oracle fails to reselect columns when table structure changes and throws ORA-01466 DBZ-9359
-
Single quotes getting double quotes in a create operation DBZ-9366
-
Mining upper boundary is miscalculated when using archive log only mode DBZ-9370
-
Oracle connector does not support large CLOB and BLOB values DBZ-9392
-
Increase max allowed json string length DBZ-9407
-
Wrong default value of task.management.timeout.ms DBZ-9408
-
LCR flushing can cause low watermark to be invalidated DBZ-9413
-
Context headers are added two times during an incremental snapshot DBZ-9422
-
Add missing destinations to Debezium Platform DBZ-9442
-
Oracle connector reselect exception handling (ORA-01555 + ORA-22924) DBZ-9446
-
Debezium server fails with CNFE DBZ-9468
-
OutOfMemory exception when recreating list of tables for snapshot callables DBZ-9472
-
Debezium Server raise "AttributeNotFoundException QueueTotalCapacity" with SqlServer source DBZ-9477
-
Getting "Unknown column in 'field list'" when column name contains backtick DBZ-9479
-
MySQL Event get header throws NullPointerException DBZ-9483
-
Adhoc blocking snapshot can leave streaming paused forever if additional-conditions is bad DBZ-9494
-
Getting "table is null" when table has no column during snapshot DBZ-9500
-
Postgres connector Fix excessive thread creation in LSN flush operations. DBZ-9501
-
Dropping primary key does not change Oracle relational metadata DBZ-9505
In total, 171 issues were resolved in Debezium 3.3. The list of changes can also be found in our release notes.
A big thank you to all the contributors from the community who worked diligently on this release:
Ahmed Bayraktar, Aleksei Silantev, Alvar Viana Gomez, Anil Dasari, Animesh Kumar, Anisha Mohanty, Artem Shubovych, Barbara Lócsi, Bhagyashree Goyal, Chirag Kava, Chris Cranford, Gabriel Cerioni, Giovanni Panice, Guangnan Shi, Harris Nguyen, Hesjona Hilaj, Indra Shukla, Jakub Cechacek, Jiri Pechanec, Joan Gomez, John Tanza, Jona J, Jonathan Schnabel, Lars M. Johansson, Liam Wu, Lucas Gazire, Luke Alexander, Marci, Mario Fiore Vitale, Matt Bayley, Nick Chomey, Olivier Chédru, Pierre-Yves Péton, Pranav Tiwari, Rajendra Dangwal, René Kerner, Robert Roldan, Seokjae Lee, Sergei Nikolaev, Shubham Kalla, Shyama Praveena S, Stefano Linguerri, Thomas Thornton, Vipin Kalra, Vojtěch Juránek, Wouter Coekaerts, and leoloel!
Chris Cranford
Chris is a software engineer at IBM and formerly Red Hat where he works on Debezium and deepens his expertise in all things Oracle and Change Data Capture on a daily basis. He previously worked on Hibernate, the leading open-source JPA persistence framework, and continues to contribute to Quarkus. Chris is based in North Carolina, United States.

About Debezium
Debezium is an open source distributed platform that turns your existing databases into event streams, so applications can see and respond almost instantly to each committed row-level change in the databases. Debezium is built on top of Kafka and provides Kafka Connect compatible connectors that monitor specific database management systems. Debezium records the history of data changes in Kafka logs, so your application can be stopped and restarted at any time and can easily consume all of the events it missed while it was not running, ensuring that all events are processed correctly and completely. Debezium is open source under the Apache License, Version 2.0.
Get involved
We hope you find Debezium interesting and useful, and want to give it a try. Follow us on Twitter @debezium, chat with us on Zulip, or join our mailing list to talk with the community. All of the code is open source on GitHub, so build the code locally and help us improve ours existing connectors and add even more connectors. If you find problems or have ideas how we can improve Debezium, please let us know or log an issue.